Data is a valuable resource for businesses and just like any other valuable resource, it needs to be managed properly. As more and more data is generated, it becomes increasingly difficult to keep track of where it all came from, how it’s being used, and what needs to be done with it when it’s no longer needed. This is where data lifecycle management (DLM) comes in.
Getting to grips with DLM is vital for any business that wants to make the most of its data. In this guide, we’ll explain what it is, detail each of the five phases of DLM, and look at the benefits it can bring to your business. We’ll also provide some tips on how to get started with DLM.
| What is data lifecycle management? |
|---|
| DLM is the process of managing data throughout its entire lifecycle, from its creation to its eventual deletion. The goals of DLM are to ensure data is stored securely and efficiently, that it is accessible when needed, and that it is disposed of correctly when no longer required. |
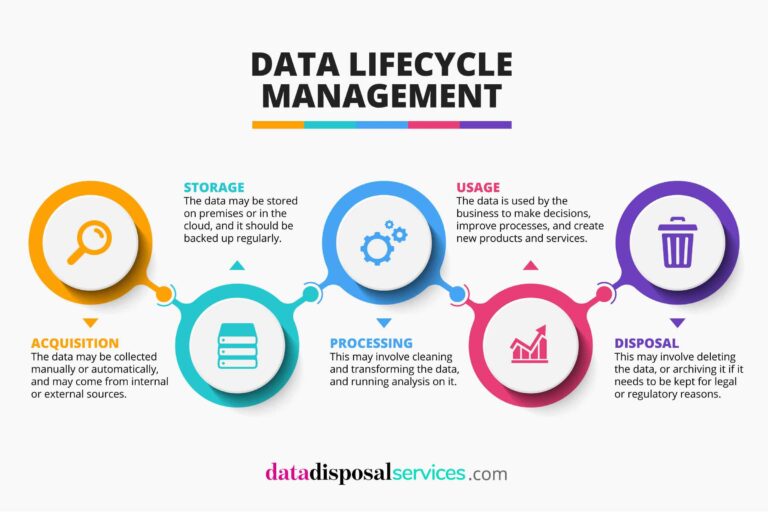
The five phases of data lifecycle management
DLM can be broken down into five distinct phases:
1. Acquisition
This is the process of acquiring data from various sources. The data may be collected manually or automatically, and may come from internal or external sources. It’s important to ensure that the data is accurate and complete, and that it meets the business’s data quality standards.
There are regulations on how data is collected and used, so it’s important to make sure you comply with these regulations.
2. Storage
Once data has been acquired, it needs to be stored securely. The data may be stored on premises or in the cloud, and it should be backed up regularly. It’s important to choose the right storage solution for your data, and to make sure that it is accessible when needed.
3. Processing
The data needs to be processed so that it can be used by the business. This may involve cleaning and transforming the data, and running analysis on it.
This could be statistical analysis, data mining, or machine learning. The quality of the data will affect the accuracy of the results, so it’s important to make sure that data is of a high quality.
4. Usage
The data is used by the business to make decisions, improve processes, and create new products and services. It must be available to the people who need it, when they need it.
There should be policies in place on how the data is shared and used, to ensure that it is used appropriately. This is because data could be used in a report, dashboard, or visualisation, which may also need to be shared with other businesses or outside organisations.
5. Disposal
When data is no longer needed, it must be disposed of correctly. This may involve deleting the data, or archiving it if it needs to be kept for legal or regulatory reasons. Data that is no longer used but may be useful later should be stored securely and have a clear policy on its storage.
Benefits of data lifecycle management
There are many benefits to implementing data lifecycle management, including:
Improved data security
DLM helps to ensure that data is stored securely and that it is disposed of correctly when no longer needed. This helps to protect businesses from data breaches and other security threats.
Improved data quality
DLM helps businesses to keep track of their data and ensure that it is of a high quality. This can help to improve the accuracy of data-driven decision-making.
Improved efficiency
DLM helps businesses to use their data more effectively by ensuring that it is stored securely and efficiently, and that it is accessible when needed.
Improved compliance
DLM can help businesses to comply with data-related regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
How to get started with data lifecycle management
There are a few things you need to do to get started with data lifecycle management:
- Define your data governance policy: This should detail how data will be managed throughout its lifecycle.
- Identify your data sources: You need to know where your data is coming from so that you can properly manage it.
- Implement data management processes: This includes things like data backup, data archiving, and data disposal.
- Train employees: It’s important to ensure that all employees are aware of your data governance policy and know how to comply with it.
Data lifecycle management is a vital process for businesses that want to make the most of their data. By following the steps above, you can get started with DLM and reap the many benefits it has to offer.
FAQs
DLM is the process of managing data throughout its entire lifecycle, from its creation to its eventual deletion.
The goals of DLM are to ensure data is stored securely and efficiently, that it is accessible when needed, and that it is disposed of correctly when no longer required.
The five phases of data lifecycle management are acquisition, storage, processing, access, and disposal.
There are many benefits to implementing data lifecycle management, including improved data security, improved data quality, improved efficiency, and improved compliance.
There are a few things you need to do to get started with data lifecycle management: define your data governance policy, identify your data sources, implement data management processes, and train employees.